
Respect my work! or BTC: 1MTFbBSKrocPK7G6GKfG8RoTw5N57WnnNa  If you have paid donate send me e-mail with Your data or transaction number to receive an access code to articles with limited access. |
PmWiki /
Creating report of type InternalShortcut tableGeneral concept of Internal reportsReport of type Internal it build from blocks called Elements. These elements are distributed in hierarchy that sets execute order sections grouped into blocks. Important!
One of the sections if SQL field, thanks to which in Internal reports it is possible to use multiple SQL queries. There are no limitations in that matter. When registering element, it's distribution is decided by value entered in field Weight. Elements can be nested, meaning that for every element user can point another element, so called Master element. When registering report processing section of elements goes in recursive manner, meaning that at first elements are processed based od hierarchy (ascending weight), next elements without set master elements (unless when processing element it turns out that thus element is parent to other elements. In that case algorithm shifts to child elements processing (here you can learn od details)). For child elements the hierarchy is set relative to master element. Let's look at below example: After processing elements A and B section C is processed. Important!
Considering that element C is conditional element (IFTHEN), then it's child elements will be processed only if processing instruction in element C will set variable $status value 1. Otherwise after processing element C element H will be processed. On below image elements D,E and G are considered as child of C element and their hierarchy is set accordingly: D=1,E=2 and G=3 what means that first in order to process is element D (and all his child elements - in this case no such elements), then element E (and all his child elements - in this case element D) and then element G (and all his child elements - in this case no such elements). 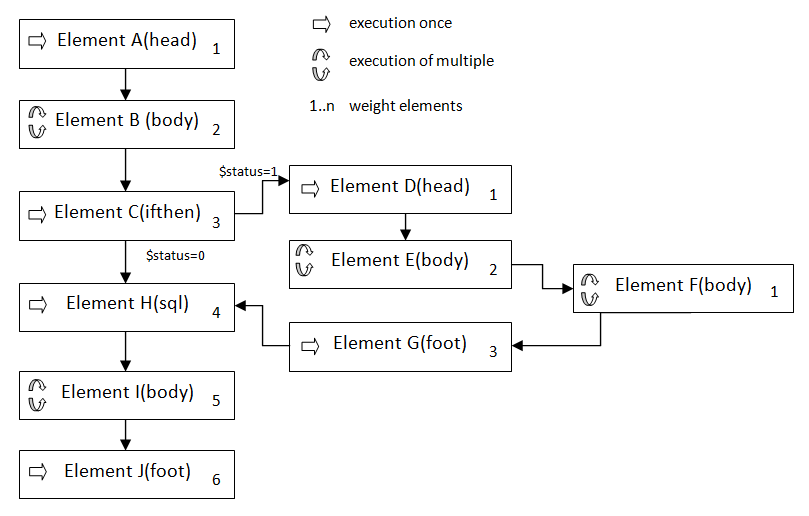 Case is different for elements E and F. Both of them are blocks of multiple processing and element E is unconditionally master element to element F, meaning processing element F will always have place. Important!
Whether block is single processing block or multi processing block determines SQL query linked with given elements. If it return multiple rows, then this elements is multiple processing element. Otherwise, if SQL field is empty or SQL query entered in this field returns only one row this element is single processing element. Only exception is IFTHEN clause that always is single processing element. In this case after processing each element E (number or processings is equal to number of rows returned by SQL query in SQL section of this element) goes multiple processing element F what can be illustrated by following pseudo code:
FOREACH ELEMENT E
.........
FOREACH ELEMENT F
........
END FOREACH
END FOREACH
In mentioned example while generating report there are 2 possible scenarios of element analysis: a) when in element C variable $status will be set to 1 processing order will be following: A,B,C,D,E,F,G,H,I,J b) when in element C variable $status will be set to 0 processing order will be following: A,B,C,H,I,J As you can see thanks to conditional element IFTHEN you can decide what elements and when will be processed. Thanks to that we gain high flexibility in terms of final report look. Element typesIn ProReports system are defined following types:
Element schema - sectionsEach element is build from the same sections (fields):
Important!
The stored procedure (PL/SPL) used in this section, must return one row of data though. Hint!
If the stored procedure will create temporary tables, they can be used in next elements of the report.
Processing element section while generating a reportProcessing each element in report of type Internal goes according to below algorithm: 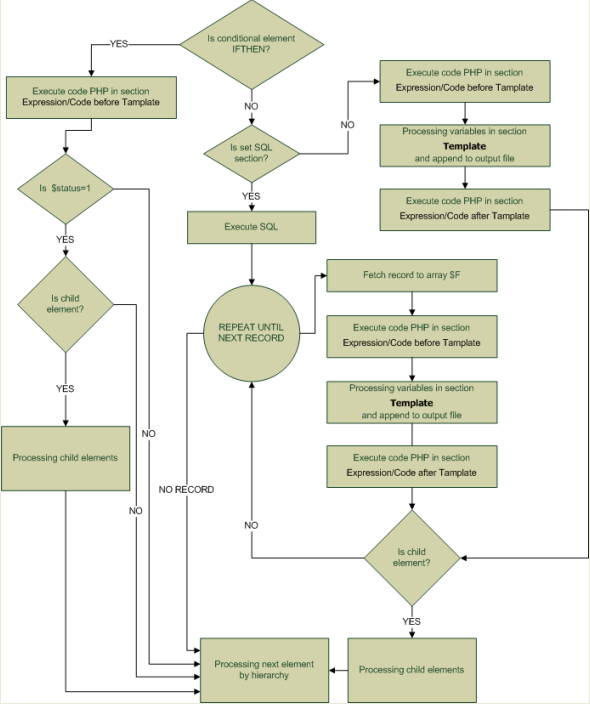 From algorithms described above emerges that only Template section is attached to result file and has direct influence on final result. However equally important is freedom of filling in sections Expression/Code before Template and Expression/Code after Template' with any PHP code, what creates infinite possibilities of building a report. Associate tables on element sectionsIn sections:
of every element while creating report you can use predefined association tables: $P - table with parameters passed from form, e.g. when in form was field Date then, it's value will be passed as $P[Date] $F - table with values of row's fields that was returned by SQL query defined in section SQL of element. Every iteration (look processing algorithm) sets date for another row. Following convention is used: Important!
Symbol needs to be entered as it was defined in element (case sensitive) and name field must be entered in lower case only. e.g. $F[A_login] (A- section Symbol of element, login - field name). Important!
In table $F current record of master element is available for child elements and can be used in constructing SQL query in SQL sections of child elements. For example, in section SQL of child element B you can use: SELECT year FROM years WHERE age="$F[A_age]" where $F[A_age] - value set in master element of A. $V - in this table you can create any variables which scope is global, meaning that variable created in certain element is available i every other element that is processed after element that defines this variable. Variables can be defined in following sections:
e.g. $V[data]=date("Y-m-d") defines current date. Important!
If you don't want for variable to have global scope then in sections mentioned above you can create PHP variable in regular way, e.g.:
$data=date("Y-m-d")
Hint!
If you want to put in report user's login that in section Expression/Code before Template of first element you have to enter: global $login ; $V[login]=$login ; Thanks to this, variable $V[login] can be used in any section of any element. Hint!
If you want to show content of all following association tables $P,$V i $F you have to set output format to TXT for report and in last element of section Expression/Code after Template enter: var_dump($P); var_dump($V); var_dump($F); And then perform report generation. Output file will contain information about tables content. This page may have a more recent version on pmwiki.org: PmWiki:RepInternal, and a talk page: PmWiki:RepInternal-Talk. |